Pascal's Triangle II LeetCode Solution in Java
Problem description :
Return particular row index of Pascal's Triangle based on given index.
Sample input and output :
Input 1 :
4
Output 1 :
[1, 4, 6, 4, 1]
Input 2 :
7
Output 2 :
[1, 7, 21, 35, 35, 21, 7, 1]
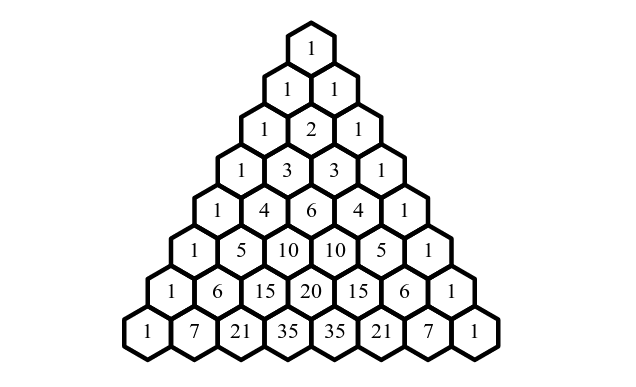
In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above. You can see in above image.
Lets see solution.
Solution 1 : Using Java List
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PascalsTriangle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter row");
int row = sc.nextInt();
int[] array = new int[row];
print(row);
}
public static void print(int row) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= row; i++) {
list.add(1);
for (int j = i-1; j > 0; j--) {
list.set(j, list.get(j) + list.get(j-1));
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
Output :
Enter row
4
[1, 4, 6, 4, 1]
Enter row
10
[1, 10, 45, 120, 210, 252, 210, 120, 45, 10, 1]
Output explanation :
- row = 4, i = 0, 0 <= 4 becomes true
- list.add(1) | list = [1]
- j = -1, -1 > 0 becomes false
- i = 1
- list.add(1) | list = [1, 1]
- j = 0, 0 > 0 becomes false
- i = 2
- list.add(1) | list = [1, 1, 1]
- j = 1, 1 > 0 becomes true
- list.set(1, list.get(1) + list.get(1-1)) | list.set(1, 2) | set 2 at index 1
- list = [1, 2, 1]
- i = 3
- list.add(1) | list = [1, 2, 1, 1]
- j = 2, 2 > 0 becomes true
- list.set(2, 3) | set 3 at index 2
- list = [1, 2, 3, 1]
- j = 1, 1 > 0 becomes true
- list.set(1, 3) | set 3 at index 1
- list = [1, 3, 3, 1]
- i = 4
- list.add(1) | list = [1, 3, 3, 1, 1]
- j = 3, 3 > 0 becomes true
- list.set(3, 4) | set 4 at index 3
- list = [1, 3, 3, 4, 1]
- j = 2, 2 > 0 becomes true
- list.set(2, 5) | set 6 at index 2
- list = [1, 3, 6, 4, 1]
- j = 1, 1 > 0 becomes true
- list.set(1, 4) | set 4 at index 1
- list = [1, 4, 6, 4, 1]
- j = 0, 0 > 0 becomes false.
- i = 5, 5 >= 4 becomes false
- Print or return list = [1, 4, 6, 4, 1]
Solution 2 : Using Java Array
public static void print(int row) {
Integer[] array = new Integer[row + 1];
Arrays.fill(array, 0);
array[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= row; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
array[j] = array[j] + array[j-1];
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(array));
}
Other Leetcode and HackerRank soultions :
- Merge two sorted LinkedList Recursively in Java? Explained with Stack Trace
- Count Triplets HackerRank solution in Java with Explanation (Dictionaries and Hashmaps Problem)

Comments
Post a Comment